THEORETICAL PROBLEMS IN BINOMIAL THEOREM
1. By substituting an appropriate value for x, prove the following identities:
(a) ![]() (b)
(b) ![]()
(c) ![]() (d)
(d) ![]()
(e) ![]() (f)
(f) ![]()
(g) ![]() (h)
(h) ![]()
2. By considering the expansion of ![]() in ascending powers of x, prove the following identities:
in ascending powers of x, prove the following identities:
(a) ![]() (b)
(b) ![]()
(c) ![]() and
and ![]()
(Hint: differentiate both sides of the expansion ![]() )
)
(d) ![]() and
and ![]()
(Hint: integrate both sides of the expansion ![]() )
)
3. If ![]() is the coefficient of
is the coefficient of ![]() in the expansion of
in the expansion of ![]() , where n is a positive integer, show by differentiating the identity
, where n is a positive integer, show by differentiating the identity
(a) ![]() that
that ![]()
(b) ![]() that
that ![]()
(c) ![]() TWICE that
TWICE that ![]()
4. Write down the value of ![]() . By comparing the coefficients of
. By comparing the coefficients of ![]() on both sides of the identity
on both sides of the identity ![]() , show that
, show that ![]() . (ans: value 0).
. (ans: value 0).
5. From the identity ![]() , by considering the coefficient of
, by considering the coefficient of
(i) ![]() on both sides, show that
on both sides, show that ![]()
(ii) ![]() on both sides, prove that
on both sides, prove that ![]() .
.
6. By equating the coefficient of xr on each side of the identities ![]() and
and ![]() , prove that
, prove that ![]() and that
and that ![]() .
.
7. By considering the coefficients of xn on both sides of the identity ![]() , prove that
, prove that ![]() is equal to
is equal to
(a) 0 if n is odd; (b) 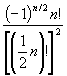 if n is even.
if n is even.
8. (i) By considering the coefficient of ![]() on both sides of the identity
on both sides of the identity ![]() , prove that
, prove that ![]()
(ii) If ![]() and
and ![]() , and by considering the coefficients of
, and by considering the coefficients of ![]() in the product
in the product ![]() to obtain the value of
to obtain the value of ![]() (ans:
(ans: ![]() )
)
(Hint: write the expansion of (1+x)n in reverse)
9. (i) By evaluating the integral ![]() in two different ways, prove the identity
in two different ways, prove the identity ![]()
(ii) Express ![]() in sigma notation. Then by eveluating the integral
in sigma notation. Then by eveluating the integral ![]() in two different ways, prove the identity
in two different ways, prove the identity ![]() where m = 2n+1. (ans:
where m = 2n+1. (ans: ![]() )
)
10. Find ![]() and hence evaluate
and hence evaluate ![]()
(i) Noting that ![]() and by using the binomial theorem to expand
and by using the binomial theorem to expand ![]() where n is a positive integer, prove that
where n is a positive integer, prove that ![]() .
.
(ii) Use the above result to find the value (rational number) of the integral ![]() .
.
(ans: ![]() (ii)
(ii) ![]() ).
).